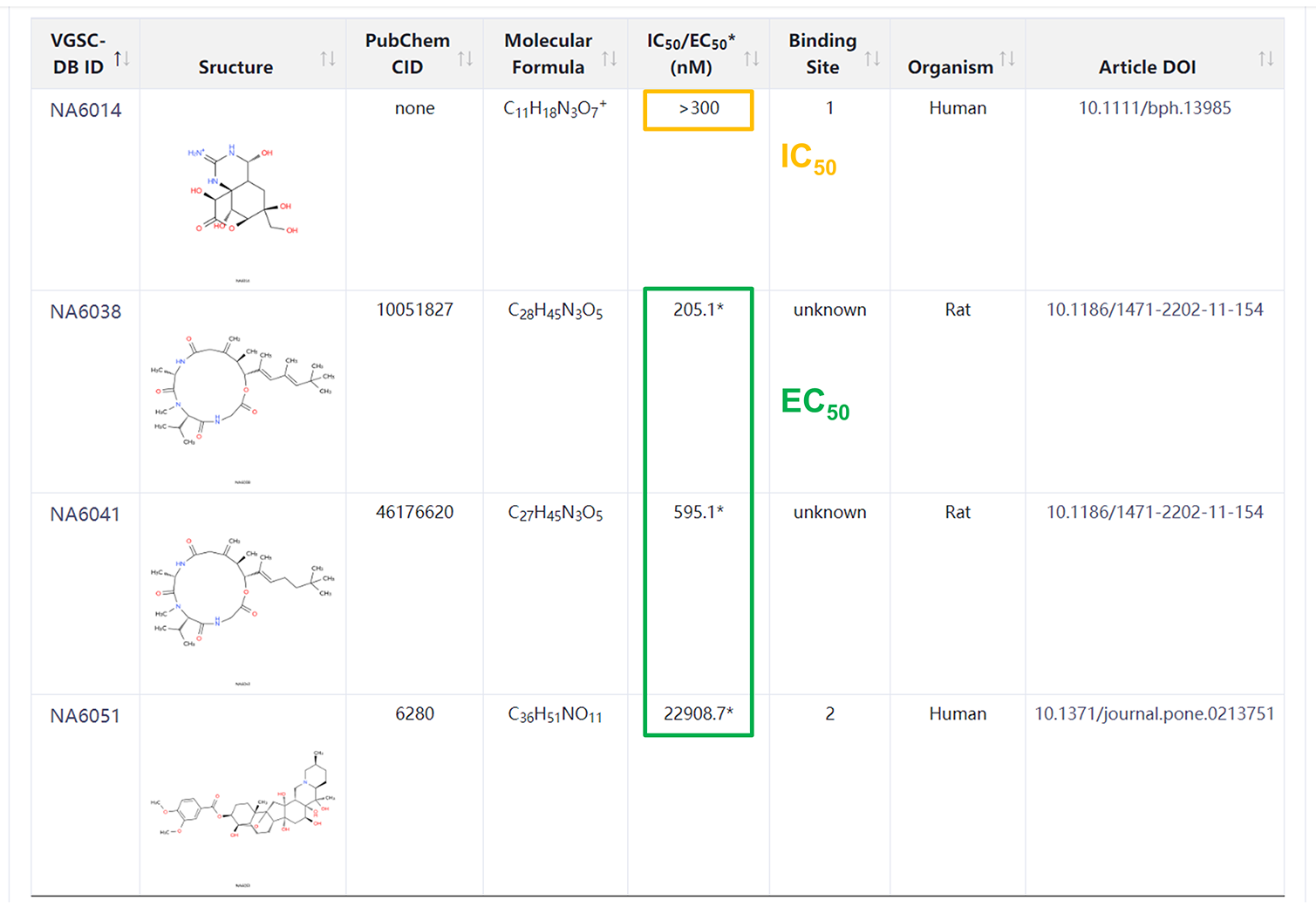
Binding Site
✔ Site1~8: Up to now, eight binding sites, which can interact with natural toxins and therapeutic drug molecules,
have been identified in the structures of VGSCs, and exhibit diverse physiological functions in response to different ligands.
✔ VSD: The VSD (voltage-sensing domain) is the important part of VGSCs, which can sense the change of external voltage and
adjust the opening of channel when the membrane is depolarized. The eukaryotic VGSCs have four VSDs (VSDI~VSDIV).
In recent years, the fourth VSD (VSDIV) has been determined as a new binding domain and several compounds targeting
this domain have entered clinical trials.
✔ In VGSC-DB, the binding site information of compounds are supplemented according to the above domain.

| Site | Ligand | Type | Binding domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tetrodotoxin (TTX), saxitoxin (STX), μ-contoxins | Extracellular pore blocker | DI~DIV P-loops |
| 2 | Batrachotoxin (BTX), veratridine (VTD), grayanotoxin (GTX), aconitine (ACT) | Intracellular pore gating activator (state dependent) | Near DI~DIV S6 (four repeats) |
| 3 | α-scorpion toxins, sea anemone toxins | Extracellular gating activator | Extracellular loops of DIV S3~S4 |
| 4 | β-conotoxin, δ-palutoxins, spider toxins | Extracellular gating blocker | Extracellular loops of DII S1~S2 and S3~S4 |
| 5 | Ciguatoxins (CTX), brevetoxins (PbTxs) | Intracellular pore gating activator (state dependent) | Near DI-S6 and DIV-S5 |
| 6 | δ-conotoxins | Extracellular gating activator | Near DIV-S4 |
| 7 | Pyrethroids | Intracellular gating activator | Near DIII-S6 |
| 8 | Small-molecule drugs, local anesthetics (LA) | LA binding site | Near DI~DIV S6 |
Biological Activity
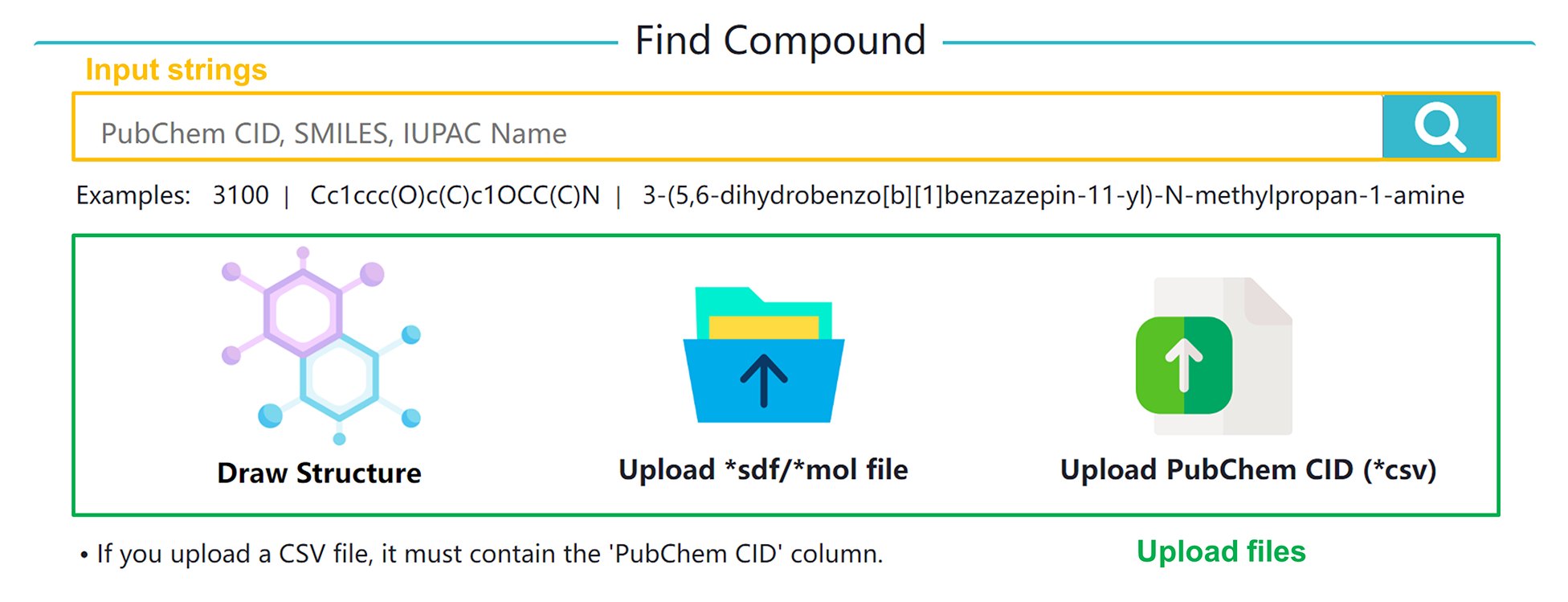
Search
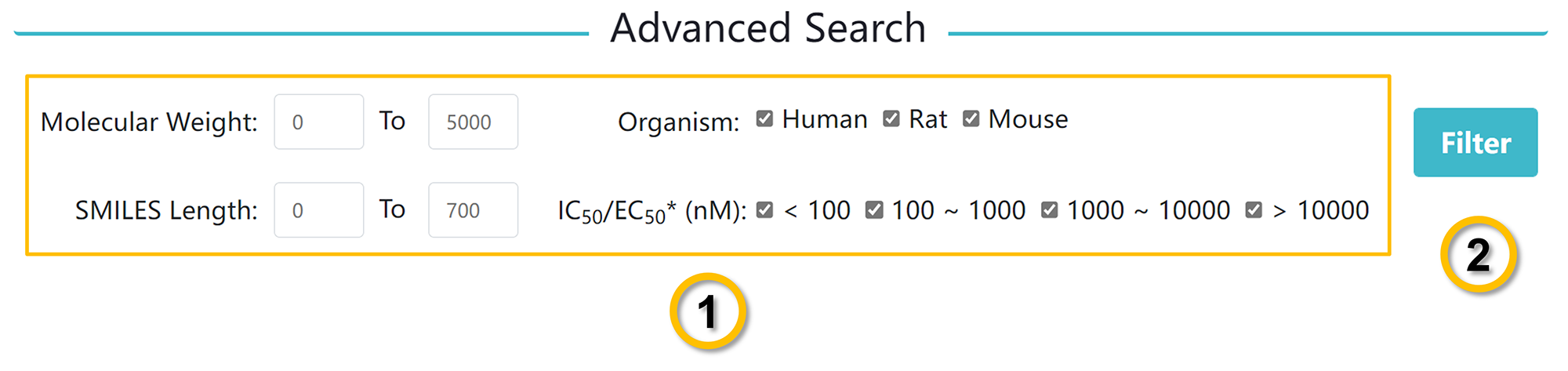
 ✔ Advanced Search: VGSC-DB provides a function for advanced searches.
A large number of compounds can be searched by selecting the molecular weight, SMILES length,
organism, and (IC50). Users can download data in batches.
✔ Advanced Search: VGSC-DB provides a function for advanced searches.
A large number of compounds can be searched by selecting the molecular weight, SMILES length,
organism, and (IC50). Users can download data in batches.
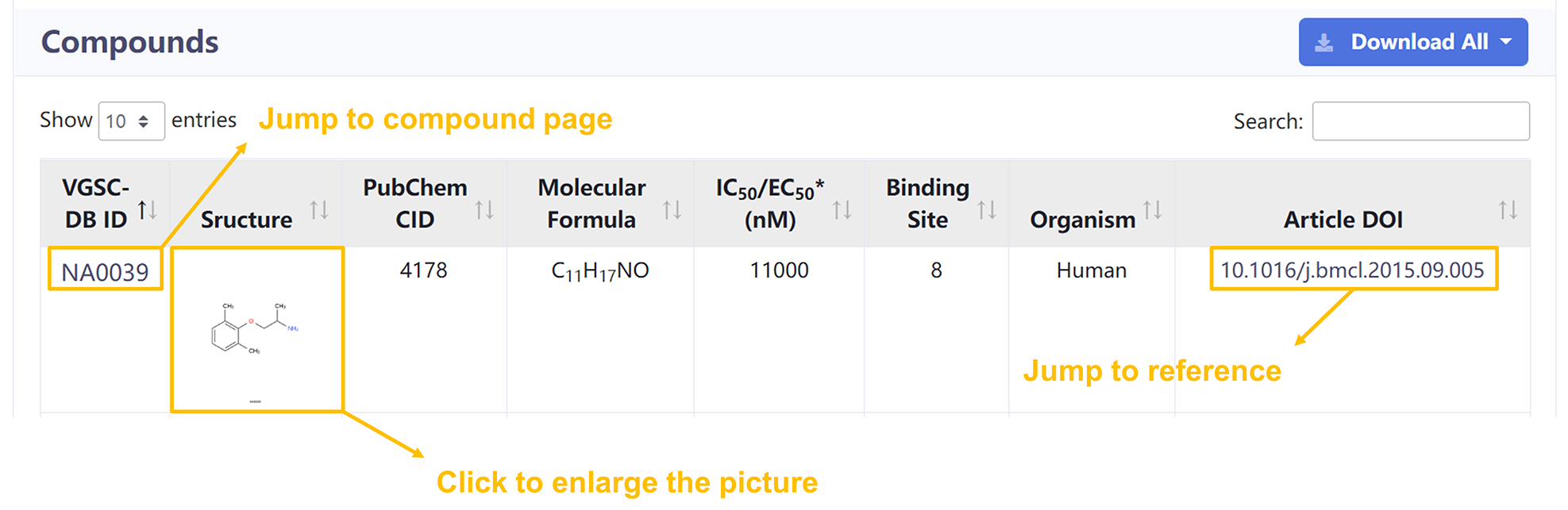
 ✔ Results: The search results are displayed in the form of small cards.
Users can view the brief information of compound and click the 'VGSC-DB ID' to jump to the compound page.
✔ Results: The search results are displayed in the form of small cards.
Users can view the brief information of compound and click the 'VGSC-DB ID' to jump to the compound page.

Data

Target Page


Compound Page

